EARLY COMPUTING DEVICES II
In the previous post, we learnt about few Early Computing Devices, in this post, you’ll see more advanced early computing devices II.
Pascal’s Calculator:
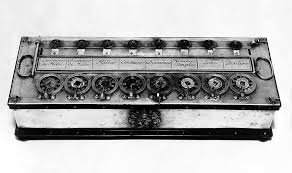
In 1642 Blaise Pascal, a French mathematician at the age of 19, built the first mechanical adding machine called PASCALINE.
Pascaline was invented to put an end to his father’s endless calculation and recalculation as a tax collector.
Uses of Pascaline:
It performs addition and subtraction of up to 8 digit number.
Components of Pascaline:
Pascaline made use of interlocking wheels and gears. It had spooked metal wheel dials with digit 0-9 displayed around the circumference of each wheel. As the first wheel completes rotation from 0-9, second wheel continued from 0-9 automatically moves to the third and continuously until calculation is completed.
Leibniz’s Stepped Reckoner:

Gottfried Von Leibniz, a German mathematician expanded on the work of Pascal’s adding machine that was time wasting.
It carries out multiplication only by repeated addition and division and through repeated subtraction.
Leibniz, in 1694 invented a mechanical multiplier, popularly known as Stepped Reckoner.
Leibniz multiplier used a cylinder bearing nine teeth of different lengths which increase in equal amounts around the drum.
Uses of Leibniz Calculator:
It can be used to multiply, divide, add, subtract and even find square root of numbers.
Components of Leibniz’s Stepped Reckoner:
It had mechanical multiplier made of cooper and steel.
Carriage was performed with a stepped wheel.
Jacquard’s Loom:

A French man known as Joseph-Marie Jacquard, in 1801 invented a machine called Jacquard’s Loom which was the first machine to run by a program.
Joseph-Marie Jacquard initiated the storage of information on punch cards. Jacquard’s loom weave more accurately and faster than any human being.
Components of Jacquard’s Loom:
It has a series of heddles, each of which is individually controlled by the Jacquard mechanism.
It uses punch cards with small holes to instruct the loom which heddles to raise.
The raised heddles allow the weft thread to pass underneath, creating the desired pattern.
Uses of Jacquard’s loom:
It simplified the process of weaving complex fabrics like damask and brocade.
Merits of Jacquard’s Loom:
Punch card technology used in the Jacquard loom was the basis for computer data storage in the 20th century.






